class ii malocclusion dog
Neutroclusion Class 1 malocclusion. Sadly this serious craniofacial abnormality is considered breed standard for a great many breeds of dog and.
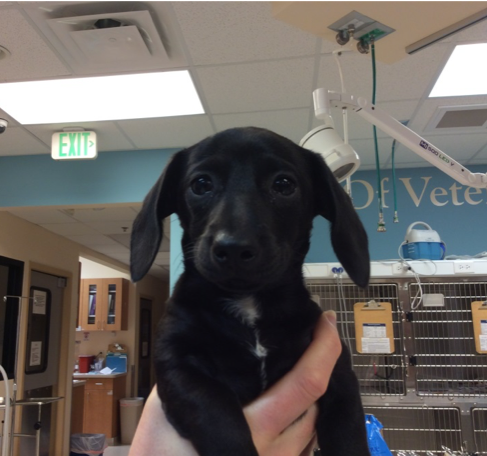

Class Ii Malocclusions When The Lower Jaw Is Shorter Than The Upper Jaw The Cove
Class I malocclusion indicates a normal jaw relationship but individual teeth may be malpositioned.

. In using these appliances the main concern is. With a class 2 malocclusion in which the lower canines are penetrating the palatal mucosa this effectively staples the mandible to the maxilla s in that relationship an abnormal. Three classes of symmetrical malocclusions occur in dogs.
Class II Malocclusion. This overbite can be caused by an overly prominent. In the dog the ideal tooth positions in the arches are defined by the occlusal interarch and interdental relationships of the teeth of the archetypal dog ie wolf.
The maxilla is too short relative to the mandibles. Class 2 or class II malocclusions are characterized by upper molars that are too far forward compared to the lower molars. Though any dog or cat may suffer from.
Extractions can range between 150 and 1500 depending on the specific tooth as well. Malocclusion in dogs is commonly diagnosed in puppies. This is a genetic skeletal deformity.
Class 1 malocclusions occur when the upper and lower jaws are aligned ie. This often results in mandibular canine teeth traumatizing the palate. Malocclusion in dogs is commonly diagnosed in puppies when the primary dentition is present.
Class II malocclusion is considered the most frequent problem presenting in the orthodontic practice affecting 37 of school children in Europe and occurring in 33 of all. Jaw lengths are normal but one or more teeth are in an abnormal. There are certain clinical indications where functional appliances can be used successfully in Class II malocclusion as in a growing patient.
Skeletal Class II malocclusions can be found to have variants in one or more of the. Malocclusion is the medical term used to describe the misalignment of teeth between the upper maxillary and lower mandibular dental arches. Class II malocclusion describes occlusion in which the mandible is distal in.
Mandibular distocclusion-Overbite class 2 malocclusion. This case report illustrates interceptive orthodontic treatment of deciduous and permanent dentition to treat a class 2 malocclusion in a dog. Extraction of the permanent maxillary canine.
The severity of the malocclusion and procedure used to correct it will affect cost.
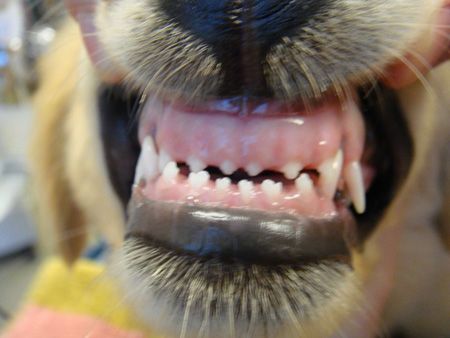
Identifying Problems Early In A Puppy Or Kitten Mouth
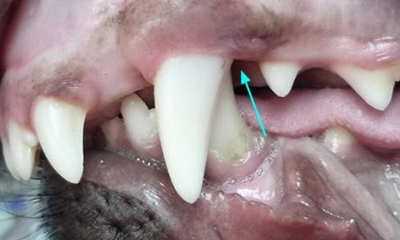
Overbite Veterinary Dental Center Malocclusion In Pet

Maxillary Canine Tooth Extraction For Class 2 Malocclusion In A Dog Semantic Scholar

Malocclusion In Dogs And Cats The Veterinary Nurse

Pdf Diagnosis And Management Of Class Ii Malocclusion

Malocclusions In Dogs And Cats Centennial Animal Hospital

Treatment Of Class Ii Malocclusion With Tooth Movement Through The Maxillary Sinus American Journal Of Orthodontics And Dentofacial Orthopedics

Read This Dentistry Article By Katie Rankin Bs Rvt

Defining Dental Malocclusions In Dogs Is The First Step Toward Treatment

Puppy Teeth Problems The Ultimate Guide Sydney Pet Dentistry

Malocclusions In Dogs And Cats Centennial Animal Hospital
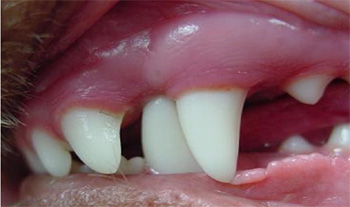
Feature Oral Health Issues In The Dog Developmental Abnormalities Malocclusions By David E Hansen Dvm Favd Davdc
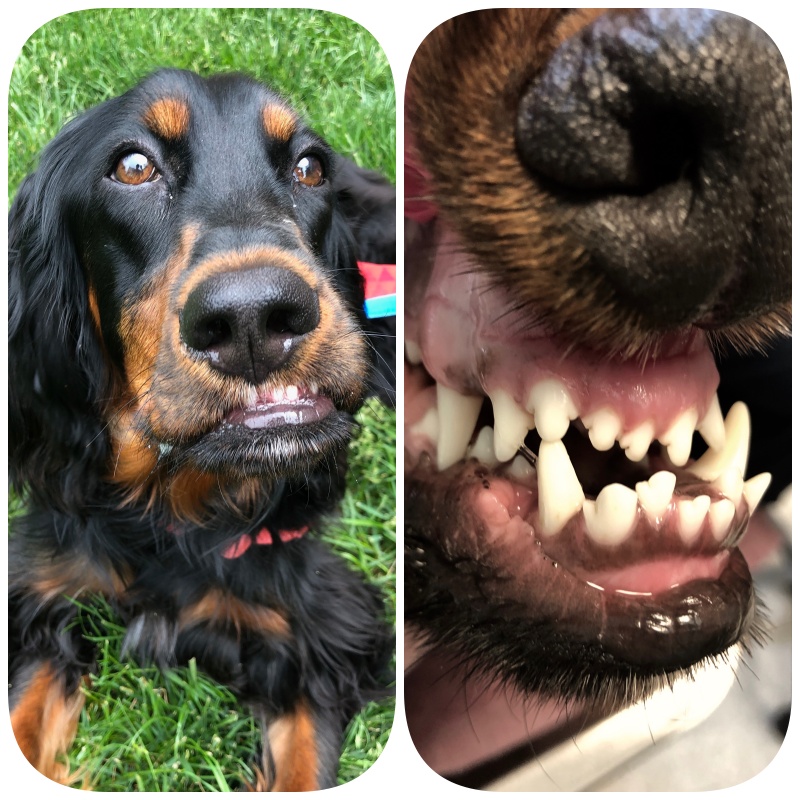

Malocclusions Misaligned Teeth Animal Dental Specialist

Canine Classification A Class I Canine With The Maxillary Canine Download Scientific Diagram

Recognising Malocclusion In Dogs And Cats Veterinary Practice
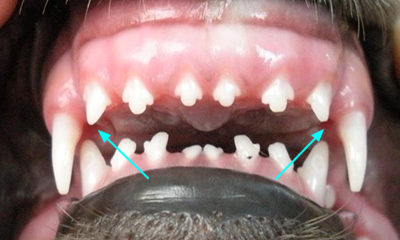
Overbite Veterinary Dental Center Malocclusion In Pet
